Healthcare data security is a critical concern in our increasingly digital world. At Scan N More, we understand the importance of safeguarding sensitive patient information from cyber threats and unauthorized access.
This blog post explores essential best practices for protecting health care data, covering key areas such as risk assessment, access controls, and secure data storage. We’ll provide practical insights to help healthcare organizations strengthen their security measures and comply with regulatory requirements.
The Biggest Threats to Healthcare Data Security
Healthcare data security presents complex challenges that evolve rapidly. The landscape of threats to sensitive medical information has transformed significantly in recent years. This chapter explores the most pressing risks that healthcare organizations face today.
Cybercriminals Target Healthcare Systems
Cybercriminals increasingly view healthcare data as a lucrative target. In 2023, 725 data breaches were reported to OCR, affecting more than 133 million records. This alarming trend underscores the need for robust cybersecurity measures.
Ransomware attacks pose a particularly severe threat. These attacks can encrypt critical patient data, disrupt care, and potentially put lives at risk. The largest healthcare data breach to date occurred in 2024, when a ransomware attack on Change Healthcare affected approximately 190 million individuals.
Insider Threats: The Enemy Within
While external attacks grab headlines, insider threats remain a significant risk. Employees, contractors, or vendors with access to sensitive data can intentionally or accidentally compromise security. Studies show that insider threats account for a significant portion of data breaches, with many stemming from employee negligence.
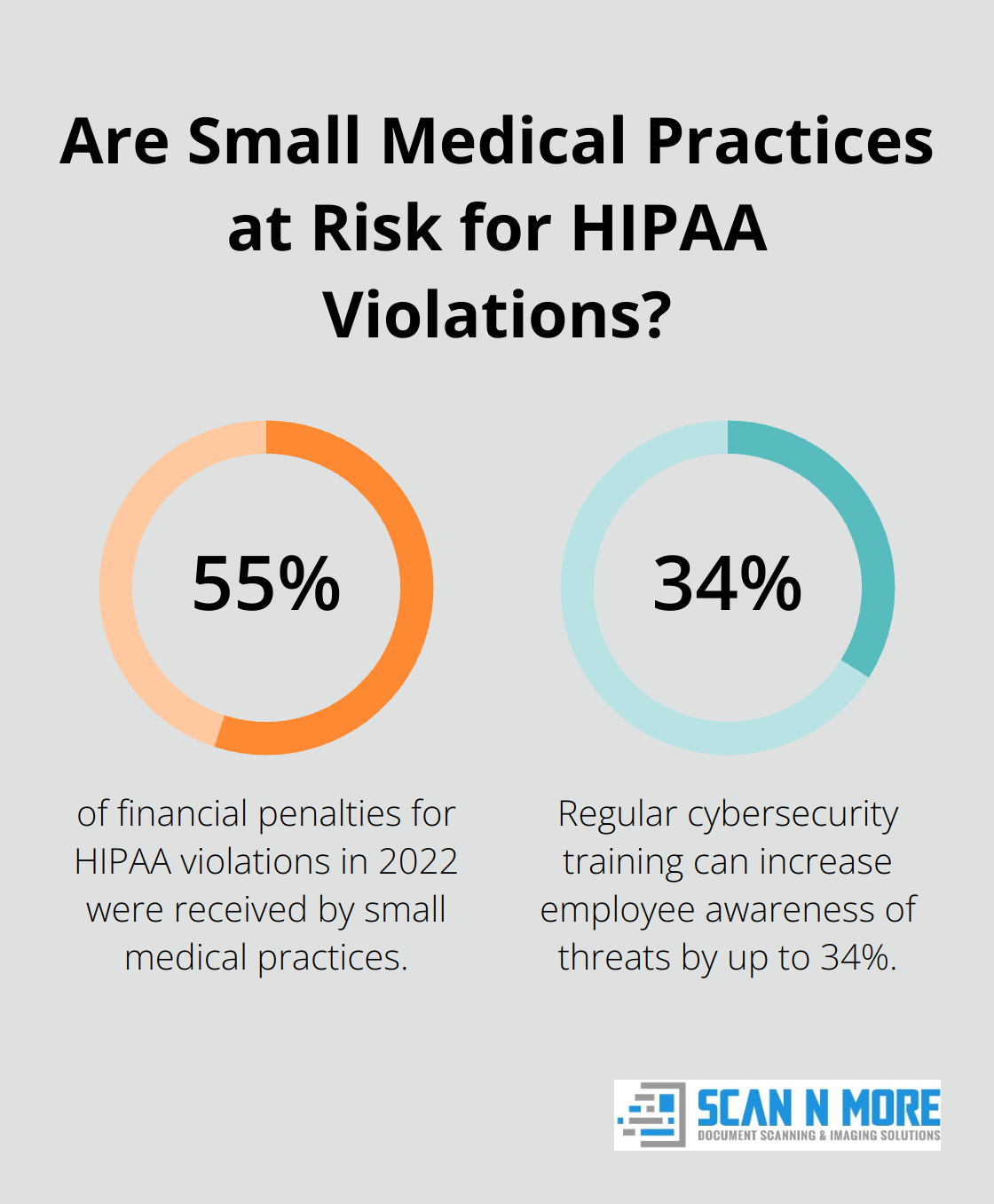
To mitigate this risk, healthcare organizations must implement strict access controls and conduct regular audits. Training staff on security best practices is essential – studies have shown that regular cybersecurity training can increase employee awareness of threats by up to 34%.
Regulatory Compliance: Navigating a Complex Landscape
Healthcare organizations must navigate a complex web of regulations designed to protect patient data. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) sets the standard for safeguarding medical information in the United States. Non-compliance can result in severe penalties – in 2022, small medical practices received 55% of financial penalties for HIPAA violations.
Beyond HIPAA, organizations may need to comply with other regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) for patients in the European Union. Healthcare providers face an ongoing challenge to stay up-to-date with evolving regulatory requirements.
Legacy Systems and Outdated Technology
Many healthcare organizations still rely on legacy systems and outdated technology, which can introduce significant vulnerabilities. These systems often lack modern security features and may no longer receive critical updates or patches. Attackers can exploit these weaknesses to gain unauthorized access to sensitive patient data.
Healthcare providers must prioritize the modernization of their IT infrastructure to enhance security. This process may involve upgrading hardware, software, and network components to ensure robust protection against current and emerging threats.
Mobile Devices and IoT Vulnerabilities
The increasing use of mobile devices and Internet of Things (IoT) devices in healthcare settings expands the attack surface for cybercriminals. From smartphones to medical monitors, these devices create new entry points for potential breaches if not properly secured.
Healthcare organizations must implement comprehensive mobile device management (MDM) solutions and strict security protocols for all connected devices. This approach should include regular security updates, strong authentication measures, and network segmentation to isolate potentially vulnerable devices.
As we examine these significant threats to healthcare data security, it becomes clear that a multi-layered approach to protection is essential. In the next chapter, we will explore effective strategies for implementing strong access controls to safeguard sensitive patient information.
How to Strengthen Access Controls in Healthcare
Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-based access control (RBAC) enhances patient data security by limiting access based on job roles and ensuring compliance with regulations. This approach ensures employees only access information necessary for their specific job functions. Organizations can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches caused by insider threats through limited access based on roles.
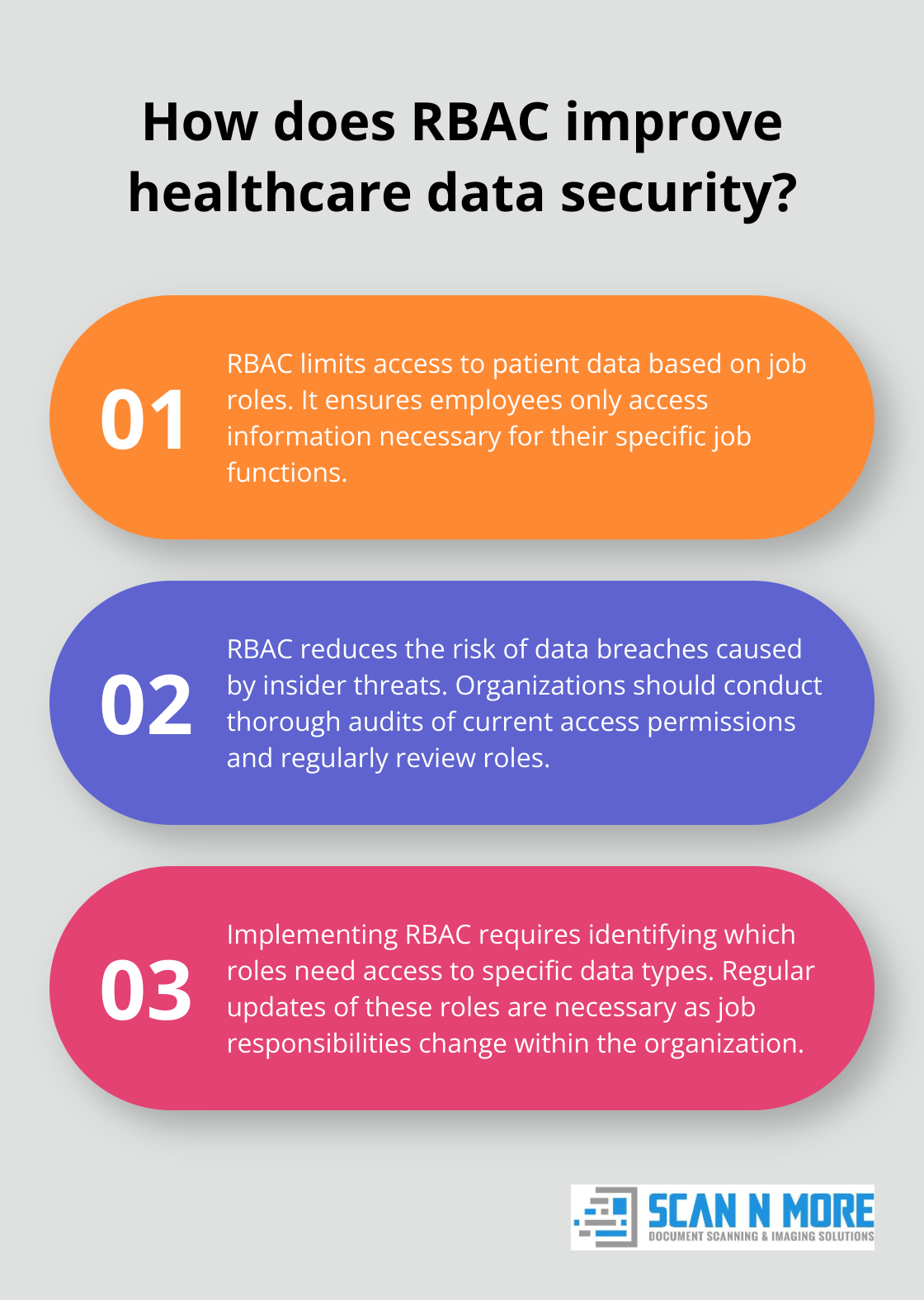
To implement RBAC effectively, organizations should conduct a thorough audit of current access permissions. They must identify which roles require access to specific types of data and adjust permissions accordingly. Regular reviews and updates of these roles are necessary as job responsibilities change within the organization.
Embrace Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security beyond traditional username and password combinations. MFA requires additional verification methods, such as biometrics or one-time codes sent to mobile devices, which significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access even if credentials are compromised.
Multi-factor authentication is crucial for enhancing security in the healthcare industry. When selecting an MFA solution, organizations should prioritize user-friendly options that won’t hinder workflow efficiency.
Conduct Regular Access Audits
Regular access audits are essential for maintaining the integrity of security measures. These audits help identify unauthorized access attempts, dormant accounts, or excessive permissions that may pose a risk to an organization’s data security.
Organizations should conduct comprehensive access reviews at least quarterly, with more frequent spot-checks for high-risk systems. Utilizing automated tools to streamline this process and generate detailed reports on user activity allows for quick identification and addressing of potential security gaps before exploitation.
Implement Least Privilege Access
The principle of least privilege access restricts user account and computing processes to the minimal level of rights necessary to perform their functions. This approach limits potential damage from accidental errors or malicious actions.
Organizations should regularly review and adjust user privileges to ensure they align with current job responsibilities. This practice helps prevent privilege creep (where users accumulate unnecessary access rights over time) and reduces the risk of insider threats.
Establish Strong Password Policies
While MFA provides an additional layer of security, strong password policies remain fundamental to access control. Healthcare organizations should enforce password complexity requirements (e.g., minimum length, use of special characters) and mandate regular password changes.
Password managers can help employees create and maintain strong, unique passwords for each system they access. These tools (which often integrate with MFA solutions) can significantly improve an organization’s overall security posture.
As we move forward in our exploration of healthcare data security, the next chapter will focus on securing data storage and transmission – another critical aspect of protecting sensitive patient information.
How Healthcare Organizations Can Secure Data Storage and Transmission
Encryption: A Powerful Defense Mechanism
Encryption transforms healthcare data into an unreadable format, which protects sensitive patient information from unauthorized access. Healthcare organizations should implement strong encryption protocols for data at rest (stored on servers or devices) and in transit (moving across networks).
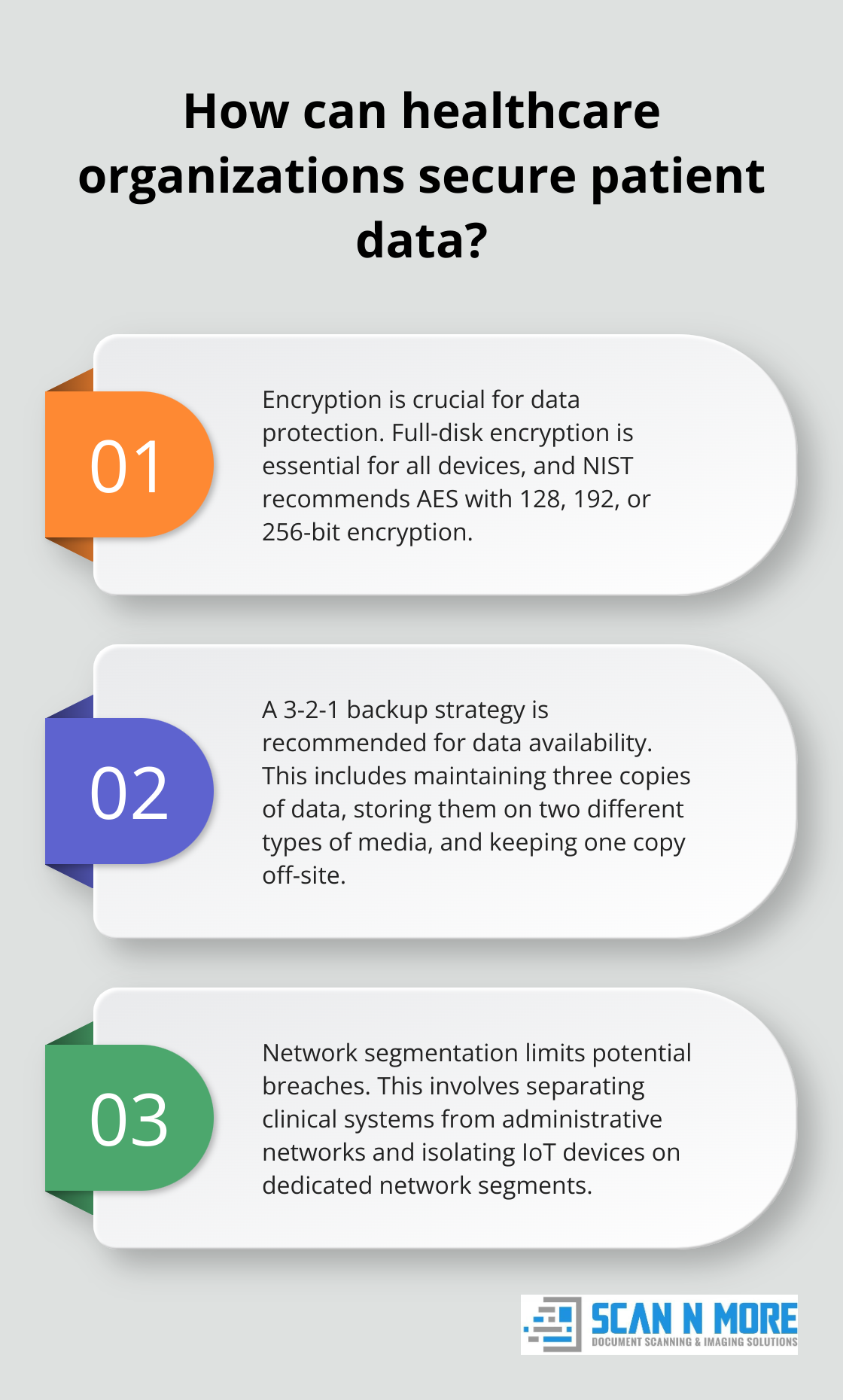
Full-disk encryption is essential for all devices that store patient information. This includes servers, workstations, and mobile devices. The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) recommends the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with 128, 192, or 256-bit encryption for optimal protection.
For data transmission, secure protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) encrypt information as it travels across networks. This protection is particularly important for organizations that use cloud services or exchange data with external partners.
Robust Backup and Recovery: Safeguarding Data Availability
Healthcare organizations must implement comprehensive backup and recovery procedures to protect against data loss. A well-designed backup strategy should include:
- Regular, automated backups of all critical systems and data
- Off-site storage of backup data to protect against physical disasters
- Encryption of backup data to maintain security
- Frequent testing of restore procedures to ensure quick data recovery
Organizations should consider a 3-2-1 backup strategy: maintain three copies of data, store them on two different types of media, and keep one copy off-site. This approach provides redundancy and protects against various failure scenarios.
Network Segmentation: Limiting Potential Breaches
Network segmentation limits the spread of potential security breaches. Healthcare organizations can contain threats and prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data by dividing a network into smaller, isolated segments.
Effective network segmentation involves:
- Separation of clinical systems from administrative networks
- Isolation of IoT devices on dedicated network segments
- Implementation of strict access controls between segments
- Use of next-generation firewalls to monitor and control traffic between segments
Network segmentation enhances security and helps organizations comply with regulatory requirements like HIPAA (which mandates access controls and audit trails for protected health information).
Secure Data Transmission Protocols
Healthcare organizations must use secure protocols for data transmission. These protocols include:
- HTTPS for web-based applications
- SFTP or FTPS for file transfers
- VPNs for remote access to network resources
These protocols (combined with strong encryption) ensure that data remains protected during transmission, even if intercepted by malicious actors.
Regular Security Audits and Assessments
Healthcare organizations should conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities in their data storage and transmission systems. These audits should include:
- Penetration testing to simulate real-world attacks
- Vulnerability scans to identify potential weaknesses
- Review of access logs and user permissions
- Assessment of encryption key management practices
Regular audits help organizations stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure that their security measures remain effective over time.
Final Thoughts
Healthcare data security requires constant vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats. Organizations must implement strong access controls, secure data storage, and conduct regular security audits to protect sensitive patient information. Staff training plays a vital role in reducing human error and creating a security-aware culture.

Future trends in healthcare data security will likely include AI-driven threat detection and enhanced protection for IoT devices. These technologies will help organizations identify and respond to risks more effectively. Mobile security will also become increasingly important as healthcare providers rely more on portable devices.
Scan N More offers professional document scanning services to transform paper-based processes into secure digital solutions. This transformation enhances both operational efficiency and data security for healthcare providers. Our expertise allows healthcare organizations to focus on patient care while maintaining robust protection for sensitive information.
